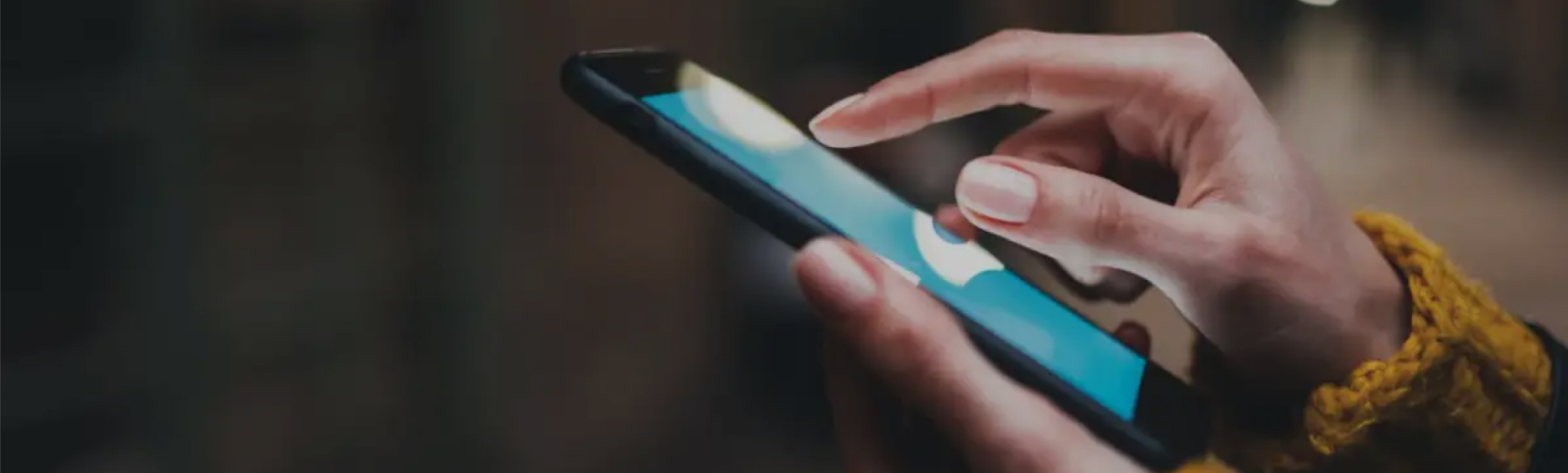
Verify and validate customers globally using their phone number.
VelocityDiscover the network provider for every mobile number globally.
AuthenticateProtect customers, accounts, and transactions within your app.
LiveDiscover if a mobile number is assigned to a subscriber.
ScoreA real time phone number credibility score.
TeleShield™Identify if a number has the propensity to be used for fraud.
Our full suite of products providing intelligence on mobile numbers.
Verify and validate customers globally using their phone number.
Discover the network provider for every mobile number globally.
Protect customers, accounts, and transactions within your app.
Discover if a mobile number is assigned to a subscriber.
A real time phone number credibility score.
Identify if a number has the propensity to be used for fraud.

A2P refers to the process of sending automated messages from an application or software to individual recipients’ mobile phones. It is commonly used for service notifications, alerts, marketing messages, and other communications.
Account takeover occurs when unauthorized individuals gain access to someone else’s online account or profile, such as email, social media, or financial accounts, by using stolen credentials or exploiting security vulnerabilities.
An alphanumeric sender ID is a form of sender identification used in messaging systems. Instead of displaying a regular phone number, an alphanumeric sender ID shows a combination of letters and numbers, allowing businesses to personalize and brand their messages when communicating with customers.
A form of fraudulent activity where deceptive or false information is used during the application process for a service, credit, or account, with the intention of gaining unauthorized benefits or advantages.
The process of verifying the identity of a user, device, or entity to grant access to specific resources or services, typically through the use of passwords, biometrics, tokens, or other security measures.
A unique alphanumeric code issued after successful authentication, granting permission for a user or application to access specific resources or perform certain actions.
Anti-Money Laundering. A set of laws, regulations, and procedures designed to prevent and detect activities related to money laundering and the financing of criminal activities.
A security mechanism that dynamically adjusts the level of authentication required based on risk factors such as user behavior, location, or device used, providing a more personalized and secure authentication process.
A technology that identifies and recognizes the type of device accessing a service or application automatically, helping to tailor the user experience and security measures accordingly.
Application Programming Interface. A set of rules and protocols that allows different software applications to communicate and interact with each other, enabling the exchange of data and functionality between systems.
This is a social engineering scam carried out using a real-time payments system. Fraudsters trick an individual or business into authorising a transfer of money to the scammers bank account, then disappear.
B
A bot is short for robot and refers to a computer program or software application that performs automated tasks. Bots are designed to execute specific actions, often repetitive or routine, without human intervention.
A behaviour score is a numerical rating or metric used to assess and quantify the behaviour of a user, customer, or entity in a particular context. It is commonly used in various fields, such as cybersecurity, finance, and marketing, to evaluate patterns of behaviour and determine the level of risk or suitability associated with an individual or entity.
C
Chargeback fraud occurs when a consumer makes a purchase using a credit card or digital payment method, receives the goods or services, but then disputes the charge with their bank or payment provider to obtain a refund. It is a deceptive practice that can lead to financial losses for merchants, especially in e-commerce, as they are often held responsible for the disputed amount.
A cloud contact centre is a customer service platform that operates in the cloud, meaning it is hosted on remote servers and accessed through the internet. It enables businesses to handle customer interactions, such as phone calls, emails, chat, and social media inquiries, with enhanced flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional on-premises contact centres.
Card-not-present fraud is a type of financial fraud that occurs when a credit or debit card is used for a transaction where the physical card is not presented, such as online or over the phone. Since the cardholder’s identity cannot be immediately verified, it poses higher risks for merchants, making them more susceptible to fraudulent transactions.
Continuous authentication is a security approach that constantly monitors and verifies a user’s identity throughout their entire session or interaction with a system. It goes beyond traditional one-time authentication methods and uses various factors, such as behaviour patterns, biometrics, and device characteristics, to ensure ongoing security and protect against unauthorised access or fraudulent activities.
D
Digital Identity refers to the electronic representation of an individual or entity’s unique characteristics and attributes within the online world. It includes personal information, authentication credentials, and other relevant data used to establish and verify one’s identity for various digital interactions and transactions.
Digital Onboarding is the process of registering and verifying new users or customers in digital platforms or services. It typically involves collecting and verifying identity information, performing security checks, and setting up the necessary accounts or access privileges to enable users to use the digital service.
A device in the context of technology refers to any physical or virtual gadget, tool, or instrument capable of performing specific functions or tasks. Devices can range from smartphones, computers, and tablets to IoT (Internet of Things) devices like smartwatches, smart home appliances, and industrial sensors.
Device Management involves the administration and monitoring of devices within a network or system. It includes tasks like provisioning, configuring, updating, and troubleshooting devices to ensure they operate efficiently, securely, and in compliance with organisational policies.
Device Cloning is the process of copying the identity of a device (Device ID) and assigning it to a similar device that is controlled by the fraudster. Cloned devices are used maliciously to deceive systems or security measures, and may impersonate legitimate ones leading to unauthorised access or fraudulent activities.
A Device ID is a unique identifier assigned to each individual device within a network or system. It enables the differentiation and tracking of devices, helping with security, management, and data analysis for various applications and services.
E
F
Fraud refers to deceptive or dishonest activities conducted with the intent to gain unauthorised benefits or cause financial or reputational harm to individuals, organisations, or businesses. In the context of telecom, fraud can involve unauthorised use of private information, identity theft, or unauthorised access to services.
Fraud Prevention encompasses strategies, processes, and technologies implemented by a company to detect, deter, and mitigate fraudulent activities within their telecom services. This includes measures such as robust authentication methods, real-time monitoring of suspicious behaviour, and data analytics to identify and stop fraudulent attempts, safeguarding private information and maintaining the trust of customers.
G
GSM, or Global System for Mobile communications, is a widely used standard for digital cellular networks used in mobile communication around the world. It provides the framework for voice and data services in mobile phones and other wireless devices. GSM networks allow users to make calls, send text messages, and access data services like internet browsing and email, making it one of the foundational technologies for modern mobile communication.
H
HLR Lookup, or Home Location Register Lookup, is a telecom process that allows businesses or service providers to query the central database of a mobile network to retrieve real-time information about a mobile phone number. This information includes details about the mobile subscriber’s network status, roaming status, and whether the number is active or disconnected. HLR Lookup is commonly used for mobile number verification, ensuring the accuracy of phone numbers, and optimising communication services by verifying and filtering mobile phone numbers before sending messages or making calls.
I
Identity-as-a-Service (IDaaS) is a cloud-based service model that provides organisations with secure and scalable identity management solutions. It enables businesses to manage user identities, access controls, and authentication processes in a centralised and streamlined manner, all hosted on remote servers in the cloud. IDaaS solutions offer features like single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and user provisioning, allowing businesses to enhance security, improve user experience, and reduce the complexity of managing identities across various applications and services.
Identity proofing is the process of verifying and validating an individual’s identity to establish their authenticity and ensure they are who they claim to be. It involves gathering and verifying various forms of identification and personal information to prevent identity theft and fraud.
Identity verification is the act of confirming the accuracy and legitimacy of an individual’s identity information, typically by comparing it against trusted and authoritative sources. It is often used in online transactions, account creations, and other scenarios where identity assurance is crucial.
International Revenue Share Fraud is a type of telecommunications fraud where criminals exploit the revenue-sharing agreements between telecom operators to generate fraudulent call traffic and earn illicit profits. It involves making long-distance or premium-rate calls to generate revenue that is shared between fraudsters and unscrupulous international carriers.
The International Mobile Equipment Identity is a unique 15-digit number assigned to mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. The IMEI serves as a device identifier and can be used to track lost or stolen devices, block them from accessing mobile networks, and authenticate their legitimacy.
The International Mobile Subscriber Identity is a unique 15-digit number associated with a SIM card in a mobile device. It is used to identify and authenticate a subscriber on a mobile network and helps facilitate services like calls, messaging, and data access.
K
Know Your Customer (KYC) is a regulatory process used by businesses and financial institutions to verify and understand the identity of their customers. It involves collecting and verifying information, such as identification documents, address proof, and financial history, to ensure that customers are legitimate and not involved in illicit activities like money laundering or terrorism financing. KYC helps mitigate risks, comply with regulations, and build trust between businesses and their customers.
L
A long code phone number refers to a standard 10-digit phone number that is used for person-to-person communication, similar to regular phone numbers. Long codes are typically assigned to individuals or businesses for every day phone calls and text messaging purposes. Unlike short codes, which are shorter and used for mass messaging or automated services, long codes are more suitable for personal or low-volume communications due to their limited capacity for high-volume messaging.
M
Multi-factor authentication is a security method that requires users to provide two or more types of credentials to verify their identity. These credentials can include something the user knows (password), something they have (smartphone or token), and something they are (biometrics). MFA enhances security by adding layers of protection against unauthorised access.
MSISDN stands for “Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Number” and refers to a mobile phone number. It is a unique identifier assigned to a mobile device and is used for routing calls and messages to that device on a mobile network. All numbers conform to the E.164 international standard to ensure that they don’t clash with one another.
Mobile authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user accessing a mobile device or service. It can involve various methods, such as PINs, passwords, biometrics, or one-time passcodes, to ensure secure access to mobile applications and services.
Mobile Country Code is a three-digit code that identifies the country where a mobile network is registered. It is an essential part of a mobile network’s identification and is used in conjunction with the Mobile Network Code (MNC) to uniquely identify a mobile operator within a specific country.
Mobile Network Operator refers to a company or entity that provides mobile telecommunications services to customers. MNOs own and operate the infrastructure, such as cell towers and switching centres, that enable mobile communication within their coverage areas.
Mobile Number Portability is a service that allows mobile phone users to switch between different mobile operators while retaining their phone numbers. It enables users to change carriers without changing their contact information.
Mobile Network Code is a three-digit code that identifies a specific mobile network within a country. It is used in combination with the Mobile Country Code (MCC) to identify mobile operators in a given country.
MNP lookup is a process that allows businesses and service providers to check whether a mobile phone number is eligible for mobile number portability. It helps determine if a user can switch to a different mobile operator while keeping their existing phone number.
Mobile Subscriber Identification Number: MSIN is the unique identification number associated with a mobile subscriber within a mobile network. It, together with the MCC and MNC, forms the complete MSISDN (mobile phone number).
N
Number Portability Query refers to the process of checking whether a phone number is eligible for mobile number portability (MNP). It involves querying a centralised database to determine if a user can transfer their existing phone number to a different mobile network while changing their service provider. This query is performed to ensure a seamless transfer for customers who wish to switch carriers while retaining their phone number.
O
One-time Password is a temporary and single-use code sent to a user’s mobile device or email to authenticate their identity during login or certain transactions. It provides an additional layer of security, as the code is valid only for a short period and cannot be reused, reducing the risk of unauthorised access.
Omnichannel messaging refers to a communication approach that integrates multiple channels, such as SMS, email, social media, and chat, to provide a seamless and consistent messaging experience for users. This strategy allows businesses to reach their customers through their preferred channels and ensure effective communication across various touchpoints.
Origin Based Rating (OBR) fraud prevention is a system used in telecommunications to prevent fraud related to international calls. It involves analysing call data and determining the call’s actual origin to prevent fraudsters from manipulating call routing and exploiting pricing disparities across different regions. By detecting and blocking suspicious traffic, telecom providers can mitigate potential financial losses from fraudulent activities.
P
P2P messaging stands for Person-to-Person messaging and refers to the exchange of text messages or multimedia messages directly between individual users, typically using their mobile phones or other messaging apps.
Phone number lookup is the process of querying a database or service to obtain information about a specific phone number. It is commonly used for verification, fraud prevention, and contact information retrieval.
Password Spray is a type of cyberattack where attackers attempt to gain unauthorised access to multiple user accounts by using a few commonly used passwords across different accounts, rather than targeting a single account with various password attempts.
Passwordless Authentication is a security method that allows users to log in or access services without the need for traditional passwords. It employs alternative authentication factors such as biometrics, smart cards, or one-time passcodes sent to mobile devices for a more secure and user-friendly login process.
Phone Ownership refers to the confirmation or validation of the identity of the owner of a mobile phone number. It is often used in customer verification and fraud prevention processes.
Phone verification is a process used to confirm the accuracy of a mobile phone number provided by a user. It typically involves sending a verification code to the user’s phone and requiring them to enter the code to complete the verification.
Porting history refers to the record of a mobile phone number’s transfers or porting activities between different mobile network operators. It tracks the history of porting requests and completed transfers for a specific phone number.
Premium Rate Number Fraud is a type of telecom fraud where attackers set up premium rate phone numbers and generate revenue by manipulating victims to make calls or send text messages to those numbers without the user’s knowledge that they are paying a premium for doing so.
R
Risk assessment is a systematic process used to identify, analyse, and evaluate potential risks associated with a specific activity, project, or situation. It involves gathering relevant data, considering potential hazards, and assessing the likelihood and potential impact of adverse events. The purpose of risk assessment is to inform decision-making, prioritise risk mitigation efforts, and ensure the safety, security, and success of the undertaking.
S
The SMS character limit refers to the maximum number of characters that can be included in a single text message (SMS). Standard SMS messages have a character limit of 160 characters. If a message exceeds this limit, it is split into multiple messages, and the sender is charged accordingly.
An SMS aggregator is a service provider that acts as an intermediary between businesses or individuals and multiple mobile network operators. It allows businesses to send bulk SMS messages to various recipients across different networks through a single interface.
SMS API stands for “Short Message Service Application Programming Interface.” It is a set of rules and protocols that enable developers to integrate SMS functionality into their applications, websites, or systems, allowing them to send and receive SMS messages programmatically.
An SMS gateway is a hardware or software system that allows the exchange of SMS messages between different telecommunications networks. It serves as a bridge between applications or computers and the mobile network, facilitating SMS communication.
SMS notification refers to the practice of sending short text messages to users’ mobile phones to provide updates, alerts, or reminders. It is widely used in various industries, including banking, healthcare, and e-commerce, to keep customers informed about important events or transactions.
An SMS number is a phone number that can receive and send SMS messages. It is used for two-way text communication between individuals or businesses.
SMS Routing is the process of determining the most efficient path to deliver an SMS message from the sender to the recipient. It involves selecting the appropriate SMS gateway or aggregator to ensure successful message delivery.
Synthetic identity fraud is a type of identity theft where criminals create fictitious identities using a combination of real and fabricated information. These synthetic identities are then used to commit fraudulent activities, such as applying for credit or opening accounts.
SIM Swap is a process where a mobile phone’s SIM card is replaced with a new one, allowing them to retain their phone number and access to their mobile network. Legitimate SIM Swap events usually occur because the user has lost their phone, or it has been stolen or they have changed network provider. However fraudulent SIM Swaps are also possible where a fraudster will move a customer number to a new SIM card that they control, either by social engineering, targeting phishing or other similar attack.
Synthetic Identity refers to a fabricated identity created using a combination of real and fictitious information. These identities are often used for fraudulent purposes, making it difficult for authorities to detect and combat identity theft.
SS7 lookup involves querying the Signaling System No. 7 (SS7) network to gather information about a specific mobile phone number, such as its location or the network it is connected to.
Strong customer authentication (SCA) is a security requirement under the Revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2) in the European Union. It mandates that online transactions must be validated using at least two out of three authentication factors: something the customer knows, something the customer has, and something the customer is.
Silent authentication is a process where a user’s identity is verified in the background without requiring them to actively participate or provide additional authentication factors. It is often used to streamline authentication for a seamless user experience.
T
Time-based One-Time Password (TOTP) is a type of two-factor authentication (2FA) that generates temporary and unique one-time passwords based on the current time and a shared secret key. Users typically use a mobile app or hardware token to generate the passwords. These passwords are only valid for a short period (usually 30 seconds) and cannot be reused, adding an extra layer of security to the authentication process. TOTP is commonly used in various online services and applications to protect user accounts from unauthorised access.
2
2FA, or Two-Factor Authentication, is a security process that requires users to provide two different forms of identification to verify their identity before gaining access to a system or service. The two factors typically involve something the user knows (like a password or PIN) and something the user has (like a smartphone or a hardware token). By using multiple authentication factors, 2FA adds an extra layer of security, making it more difficult for unauthorised users to gain access to sensitive information or accounts.
"Phone number verification plays a critical role in helping to detect and prevent online fraud. TMT ID’s TeleShield product provides easy access to global mobile data, enabling us to enhance the actionable results of our MaxMind minFraud® services."
 MaxMind
MaxMind
"BTS (Business Telecommunications Services) is successfully using TMT’s Velocity and Live services to check the status of mobile numbers. This way we make sure we optimize the performance of the service offered to our customers and ensure the quality of terminating traffic to all countries.”
 Business Telecommunications Services
Business Telecommunications Services
"Working with TMT’s TeleShield service has expanded our ability to detect fraud and minimise the risk to our business. TeleShield brings peace of mind and the opportunity to stop fraud before it affects our customers’ bottom line or the service."
 Six Degrees Labs
Six Degrees Labs
"LATRO relies on TMT’s TeleShield to provide the most up to date and reliable numbering qualification information within our fraud reporting tools, enabling us to protect our customer’s revenues and empowering them to defend themselves against fraudulent numbers."
 LATRO
LATRO
"TMT is a valued partner that enables us to manage our routing costs effectively. They proactively and continuously expand their operator and country coverage while delivering exceptional customer service. We can always count on them to achieve high-quality results and look forward to our continued collaboration."
 Global Message Service
Global Message Service
"TMT provides us with the most comprehensive numbering intelligence data through their fast and reliable Velocity and Live services. TMT is a trusted partner for us, their products ensure that we continue to optimise the best performance and service to our customers."
 Global Voice
Global Voice
"TeleShield from TMT gives 42com the power to detect and target telephony fraud scams internationally, thereby protecting our company from the financial and customer experience impacts of telecommunications fraud."
 Alberto Grunstein - CEO
Alberto Grunstein - CEO
"It has been a pleasure to work with the team at TMT. They have become an essential provider of accurate numbering data information and Number Portability services globally."
 Luisa Sanchez - VP of SMS and Messaging Solutions, Identidad Technologies
Luisa Sanchez - VP of SMS and Messaging Solutions, Identidad Technologies
"Deutsche Telekom Global Carrier uses TMT ID as one of their key suppliers for Mobile Number Portability Data services. Deutsche Telekom Global Carrier uses TMT ID’s Velocity MNP solution. This is an ultra-fast query service that optimises the routing of international voice calls and A2P messaging."
 Deutsche Telekom Global Carrier
Deutsche Telekom Global Carrier
We provide the most comprehensive device, network and mobile numbering data available
Contact us > Chat to an expert >